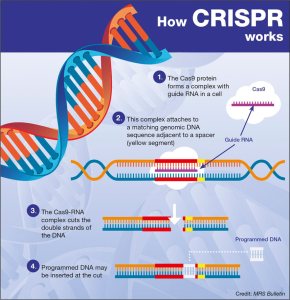
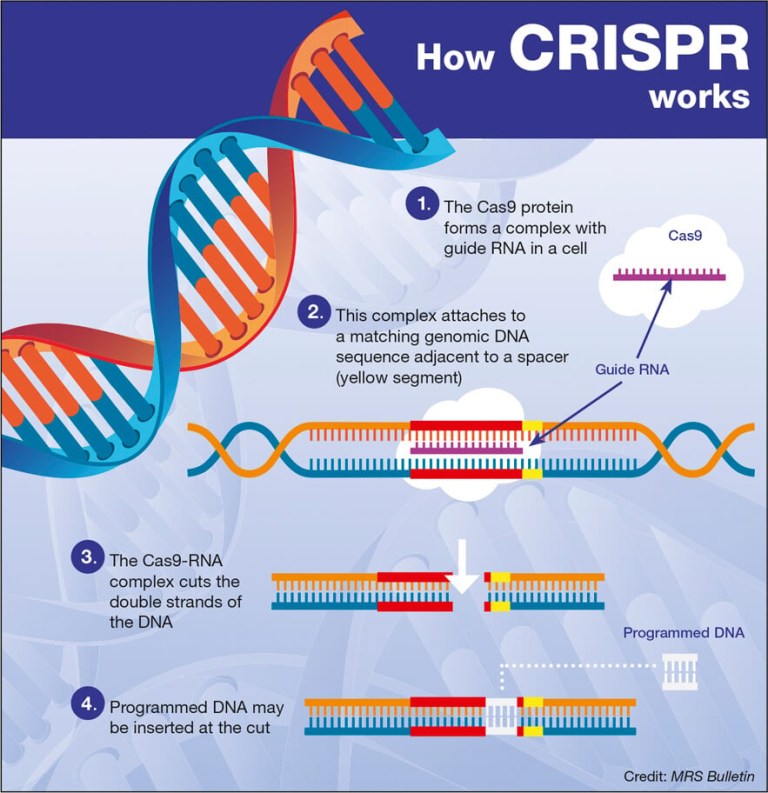
The U.S. innovation ecosystem stands as a global leader, uniquely blending academic research, federal funding, and private industry collaboration to drive advancements in technology and healthcare. Originating during World War II, this dynamic framework capitalized on public-private partnerships that facilitated groundbreaking biomedical innovations like penicillin, enhancing national resilience and global health. Over the decades, continued federal support for research has laid the groundwork for economic growth in healthcare, resulting in numerous life-saving treatments and technologies. The historical evolution of biomedical research underscores the pivotal role of strategic government funding in fostering a thriving innovation landscape. As scrutiny around funding changes grows, understanding the value of this ecosystem becomes more critical than ever for sustaining America’s position at the forefront of global biomedical advancements.
The American innovation framework is characterized by a collaborative interplay among universities, government agencies, and private enterprises, creating a vibrant atmosphere for research and development. This synergy, particularly evident in the realm of healthcare, has been enriched through federal investment strategies that shift the tide of biomedical research into an era of exponential growth. By fostering partnerships that transcend institutional barriers, the system has enabled significant breakthroughs vital for public health and economic prosperity. The legacy established during wartime has morphed into a robust model of innovation, one that continues to influence global practices in science and technology. As we explore the ongoing evolution of this aligning forces, the focus shifts to sustainability and future directions for this impressive innovation landscape.
The Historical Roots of the U.S. Innovation Ecosystem
The establishment of the U.S. innovation ecosystem can be traced back to World War II, when academic researchers and federal agencies recognized the urgent need for technological advancement in military applications. This collaboration led to remarkable breakthroughs in medicine, particularly in the development of antibiotics such as penicillin. The groundwork laid during this time fostered a culture of public-private partnerships that enhanced the capacity for biomedical innovation and set a precedent for future collaborations between government and academia. As a direct result, the United States emerged from the war with a robust innovation framework that has continued to evolve over the decades.
By engaging universities, federal agencies, and private industry from the outset, U.S. leaders were able to cultivate a synergetic environment where knowledge flowed freely and innovation thrived. This model not only accelerated technological development but also contributed to economic growth in healthcare, as investments in research translated into new treatments and medical technologies that improved patient outcomes. The cooperative spirit established during the war eventually evolved into one of the major pillars of the modern innovation ecosystem, underscoring the pivotal role of federal funding in advancing biomedical research.
Public-Private Partnerships: A Pillar of Biomedical Innovation
Public-private partnerships have become an essential element of the U.S. biomedical innovation landscape. These collaborations leverage the strengths of both sectors—government providing funding and regulatory support, and industry offering expertise and practical applications. This dynamic relationship has been instrumental in fostering breakthroughs in health technology and drug development, which are vital for combating complex health challenges. In particular, federal funding has been crucial in initiating research projects that might not have been pursued by private firms alone due to the significant risks involved.
The effective integration of public and private resources has not only led to groundbreaking medical advancements but has also stimulated economic growth in healthcare. As these partnerships evolve, they continue to adapt to the changing landscapes of both science and technology. The results of these collaborations are evident in various areas of biomedical research, from vaccine development to advanced therapeutics, illustrating the lasting benefits of a well-structured innovation ecosystem.
Federal Funding for Biomedical Research: Trends and Implications
Federal funding is a cornerstone of the U.S. innovation ecosystem, particularly in the realm of biomedical research. Historically, national funding agencies like the National Institutes of Health (NIH) have supported a wide array of research initiatives, ensuring that scientists can pursue high-risk, high-reward projects that push the boundaries of knowledge. However, recent trends show a shift in the political landscape, with proposals to cap reimbursements for indirect research costs. This could significantly impact the viability of continued innovative progress, given the reliance on federal funding for many research activities.
The implications of reduced funding are profound; without adequate financial support, research institutions might struggle to maintain their competitive edge in global biomedical innovation. Shrinking federal contributions could hinder the development of essential new therapies and decrease collaboration between public institutions and private companies, ultimately affecting the health of the American populace. The ongoing discourse around federal funding highlights the need for sensibility in policymaking, recognizing that a healthy innovation ecosystem requires commitment from all sectors.
Innovations Born from Conflict: The Role of War in Biomedical Advancements
The urgency of wartime needs has historically catalyzed significant advancements in medical science. World War II, in particular, served as a turning point for biomedical innovations, illustrating how conflict can drive research and development at unprecedented rates. The partnership between government entities and scientists during this time led to crucial breakthroughs that were essential not only for military purposes but also for civilian healthcare. The mass production of penicillin, for example, transformed medical treatment and established the foundation for modern antibiotics.
Moreover, the lessons learned from wartime necessities have continued to shape the focus and funding of biomedical research even in peacetime. The establishment of dedicated agencies, like the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD), arose from the need to coordinate medical research during the war and laid the groundwork for future initiatives. This legacy demonstrates how demands for immediate practical solutions can generate long-lasting impact, creating a robust infrastructure for ongoing innovation in the health sector.
Training the Next Generation: The Importance of Scientific Workforce Development
The impact of the U.S. innovation ecosystem extends beyond immediate technological advancements; it also encompasses the training and development of a skilled workforce in the biomedical field. Programs developed during World War II engaged thousands of young scientists, engineers, and researchers, creating a new generation capable of addressing complex healthcare challenges. This emphasis on education and training continues to be vital today, as a strong workforce is essential for maintaining the leadership of the U.S. in global biomedical innovation.
As the demand for skilled professionals in the life sciences and healthcare sectors grows, partnerships between universities, research institutions, and the federal government must adapt to facilitate the education of students in cutting-edge technological developments. Institutions that invest in advanced training programs and internships can bridge the gap between academic knowledge and practical skills, ensuring that the workforce is well-prepared to meet the evolving challenges of biomedical research and development.
From Antibiotics to Advanced Therapies: The Evolution of Drug Development
The U.S. biomedical innovation ecosystem has witnessed remarkable evolution since the mass production of antibiotics during World War II. The success of penicillin exemplified how targeted research efforts can lead to extraordinary advancements in health outcomes and set the stage for the antibiotic revolution that followed. This early success paved the way for a broader landscape of drug development, where today’s pharmaceutical companies rely on sophisticated scientific approaches to create new therapies for a multitude of diseases.
Modern drug development is characterized by more systemic and strategic methodologies, including rational drug design and biotechnology. Coupled with advancements in genomics and personalized medicine, the landscape for therapeutic development is continually expanding. The enduring legacy of wartime innovation emphasizes the need for ongoing investment in research and public-private collaboration to ensure that future generations continue to benefit from new and transformative medical interventions.
Strengthening the Model: Re-evaluating Federal Support for Research
As conversations around federal funding for biomedical research continue, there is a need for stakeholders to assess and strengthen the frameworks that support public-private partnerships. Proposals for reform should focus on maximizing the efficient allocation of funds while preserving the incentives that have led to decades of innovation. By protecting the financial mechanisms that foster collaboration among academic institutions, government, and private companies, policymakers can ensure that the U.S. continues to lead in biomedical advancements.
Moreover, fostering transparency and accountability in the distribution of federal research funds can enhance trust and cooperation between various stakeholders. By re-evaluating existing funding strategies, including the controversies surrounding indirect costs, there is a chance to create a more sustainable and productive environment for biomedical research. Ultimately, ensuring robust federal support remains vital for the continued growth and prosperity of the U.S. innovation ecosystem.
The Global Perspective: U.S. Innovation as a Model for Other Nations
The U.S. innovation ecosystem serves as a model for countries around the world, inspiring nations to focus on public-private partnerships and collaborative research initiatives. The successful integration of academic knowledge, government funding, and industrial capabilities has established the United States as a global leader in biomedical innovation. As other countries strive to develop their own innovation systems, they often look to the U.S. model for guidance on implementing effective strategies that will yield similar successes.
However, while the U.S. ecosystem has its best practices, it also faces challenges that other nations may wish to learn from. By scrutinizing the U.S. approach to federal funding, research collaboration, and workforce development, international stakeholders can gain valuable insights into what drives successful biomedical innovation. Effectively adopting and adapting these strategies can help cultivate a robust global innovation network that improves health outcomes and accelerates economic growth in healthcare worldwide.
Sustaining Innovation: Future Challenges for the Ecosystem
Although the history of the U.S. innovation ecosystem is one of great success, looking ahead, the challenges are significant. Shifts in political support for federal funding, evolving global health threats, and the rapid pace of technological change all pose potential risks to the sustainability of this ecosystem. As demands for accountability and efficiency increase, stakeholders must navigate a complex landscape to ensure continued investment in biomedical innovation.
To sustain the momentum, there will be a necessity for adaptive strategies that reinforce existing partnerships while fostering new ones. Open dialogue among researchers, policymakers, and industry leaders can facilitate a more cohesive approach to shared challenges. By prioritizing long-term investment in innovation and training, the U.S. can continue to be a beacon of biomedical research that influences global health and economic outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role does federal funding play in the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
Federal funding is crucial to the U.S. innovation ecosystem, particularly in biomedical innovation. It supports academic research, facilitates breakthroughs in medicine and technology, and strengthens public-private partnerships that drive economic growth in healthcare.
How did the history of biomedical research shape the current U.S. innovation ecosystem?
The history of biomedical research, starting from World War II, set the framework for today’s U.S. innovation ecosystem. Federal involvement through the National Institutes of Health and partnerships with universities and industries fostered advancements that have made the U.S. a leader in biomedical innovation.
What are public-private partnerships and how do they influence the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
Public-private partnerships are collaborations between government entities and private sector companies that enhance the U.S. innovation ecosystem. They facilitate shared resources and knowledge, leading to advancements in biomedical innovation and substantial economic growth in healthcare.
How does the U.S. innovation ecosystem contribute to economic growth in healthcare?
The U.S. innovation ecosystem drives economic growth in healthcare through investment in biomedical innovation, resulting in new treatments and technologies. This creates jobs, supports research initiatives, and ultimately leads to improved health outcomes, benefiting both the economy and society.
What challenges are currently facing federal funding for biomedical research in the U.S.?
Currently, federal funding for biomedical research faces challenges such as proposed budget cuts and increased scrutiny on reimbursement for indirect research costs. These changes could impact the sustainable growth of the U.S. innovation ecosystem, particularly in regards to public-private partnerships.
What is the significance of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) in the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) plays a pivotal role in the U.S. innovation ecosystem by funding biomedical research and training new scientists. Its support fosters groundbreaking discoveries and enhances collaboration between academia and industry, significantly contributing to advancements in healthcare.
How did wartime efforts during World War II catalyze the U.S. biomedical innovation system?
Wartime efforts during World War II catalyzed the U.S. biomedical innovation system by establishing foundational public-private partnerships. The urgent need for medical advancements led to significant investments in research that shaped the collaborative landscape of today’s U.S. innovation ecosystem.
What is the current state of the U.S. innovation ecosystem compared to its early days?
Today, the U.S. innovation ecosystem stands as a robust model of success, built upon decades of investment and collaboration. Compared to its early days, when biomedical research was nascent and underfunded, it now boasts a strong infrastructure of partnerships that continue to propel advancements.
Why is the U.S. innovation ecosystem considered the envy of the world?
The U.S. innovation ecosystem is considered the envy of the world due to its effective collaboration between public and private sectors, large-scale investments in biomedical research, and its proven capacity to translate scientific advancements into real-world applications, thus fostering global leadership in healthcare innovation.
What future reforms are needed to sustain the success of the U.S. innovation ecosystem?
To sustain the success of the U.S. innovation ecosystem, reforms should focus on ensuring stable federal funding, enhancing public-private partnerships, and promoting efficiency in research funding mechanisms. It’s vital to protect the established structure that supports innovation in biomedicine and beyond.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Origin of the Partnership | Started during World War II with civilian scientists aiding military technology development. |
| Role of Federal Funding | Federal funds have historically supported research, leading to advancements in medicine and technology. |
| Impact of WWII | The war created an urgent need for innovations, leading to the establishment of the Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD). |
| Breakthroughs | Penicillin production was revolutionized during the war, drastically improving military and civilian health. |
| Long-term Effects | The collaboration laid the groundwork for future biomedical advancements and contributions from young scientists. |
| Contemporary Challenges | Current focus on funding cuts for research may threaten the sustainability of the U.S. innovation ecosystem. |
Summary
The U.S. innovation ecosystem stands as a model of successful collaboration and advancement in technology and medicine. It has evolved from its roots in World War II, where a partnership between the federal government, universities, and private sectors was established to drive innovation. Today, this innovation ecosystem continues to produce significant breakthroughs, particularly in biomedicine, making it the envy of nations worldwide. As it faces challenges such as funding cuts, maintaining its structure and fostering future growth is essential to uphold its legacy and ongoing contributions to health, defense, and economic prosperity.