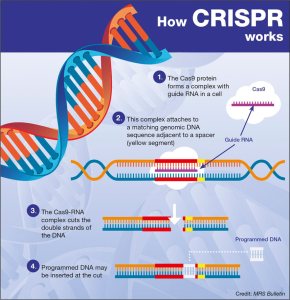
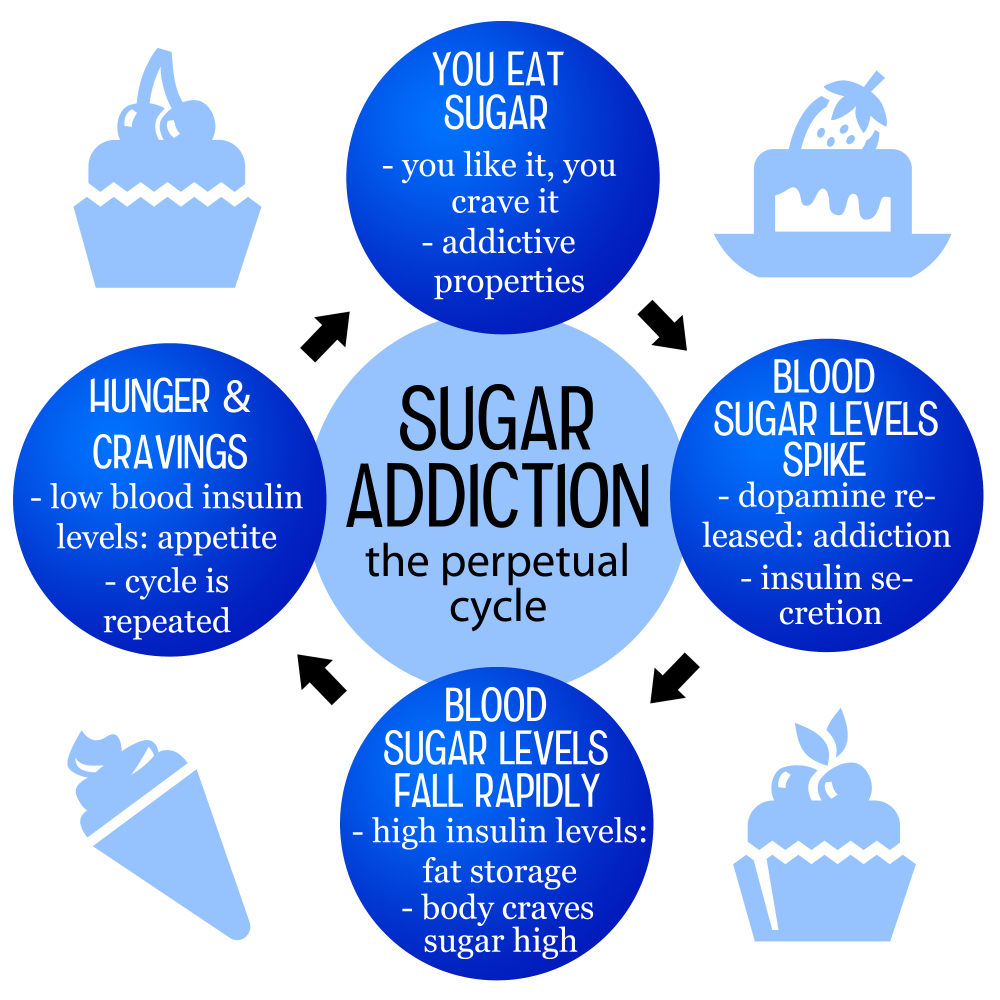
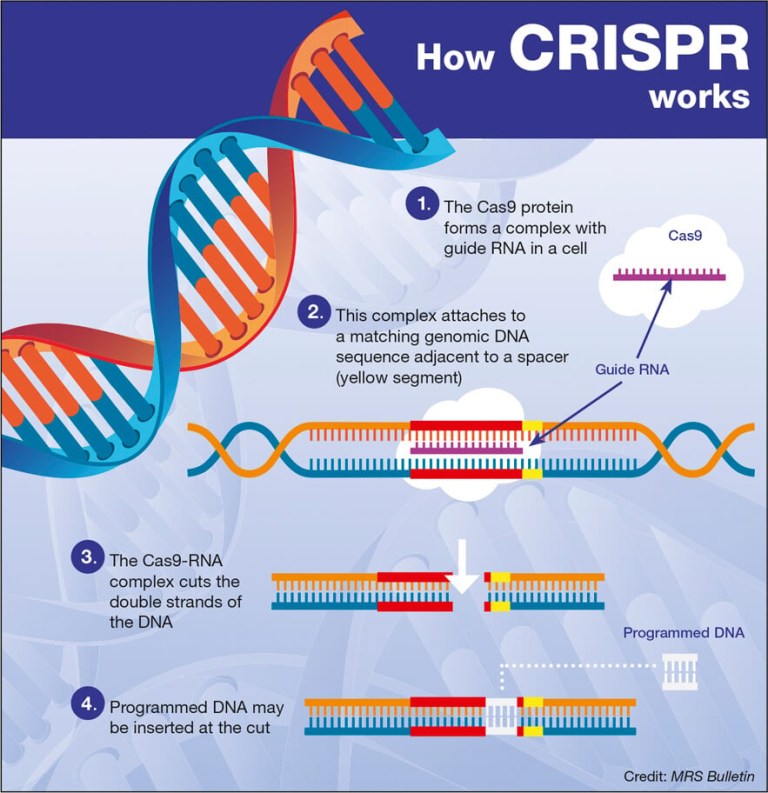
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked intense debate among nutrition experts, with researchers highlighting the profound effects of sugar on our cravings and eating behaviors. While sugar doesn’t meet the strict clinical criteria for addiction like substances such as alcohol and nicotine, its impact on our bodies is undeniable. The rise in sugar consumption, particularly in the form of ultra-processed foods, leads many to experience heightened desires for sweetness, often resulting in withdrawal symptoms like headaches and anxiety when they try to cut back. Understanding the complexity of sugar addiction is crucial, as it plays a significant role in our diets and the way we enjoy food.
The notion of sugar serving as a potential addiction is a topic worth exploring, often referred to as sugar dependence or cravings for sweet foods. Many people find themselves drawn to sugary treats, struggling with the psychological and physiological pull towards these delightful substances. As we examine the effects that excessive sweetness can have on our wellbeing, it’s important to differentiate between moderate enjoyment and compulsive behavior. With awareness of sugar consumption habits and how they can escalate into cravings, individuals can better manage their dietary choices and achieve a healthier lifestyle.
Is Sugar Addictive? Understanding the Debate
The question of whether sugar is addictive has sparked significant debate among health professionals and researchers. While substances like alcohol and nicotine are classified as addictive based on clinical criteria, sugar doesn’t receive the same classification. Nonetheless, it has been shown to provoke cravings similar to those induced by addictive substances. These cravings can lead to habitual consumption of sugar-rich foods, particularly ultra-processed ones that are easy to access and highly palatable.
As noted by nutrition experts, sugar can certainly produce withdrawal-like symptoms, such as headaches and anxiety, when consumption is suddenly halted. However, these symptoms are generally less severe compared to those associated with recognized addictive substances. This raises an important consideration: declining sugar altogether may not be feasible for most people since sugars naturally occur in many fundamental food sources, such as fruits and vegetables.
The Impact of Sugar Consumption on Cravings
Sugar consumption is intricately linked to cravings that many experience, particularly in today’s food landscape brimming with sugary snacks and drinks. The body’s response to sugar can trigger a cyclical pattern of craving and consumption that is hard to break. When we indulge in sugary foods, our brain is flooded with dopamine, the ‘feel-good hormone,’ reinforcing the pleasure associated with sugar intake. Over time, this can lead to patterns of compulsive eating, further intensifying cravings.
Moreover, the accessibility of ultra-processed foods packed with added sugars can make it incredibly challenging to reduce cravings. As the average American consumes nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar daily, recognizing the impact of this consumption on health is vital. Gradually reducing sugar intake, rather than cutting it out completely, may help alleviate cravings without the harsh withdrawal symptoms that can occur.
Sugar Withdrawal Symptoms and Their Realities
There is growing recognition of the withdrawal symptoms that some individuals experience after reducing their sugar intake. These symptoms can include headaches, fatigue, irritability, and cravings for sugary foods. This aligns with observations made by experts, who emphasize that even though sugar isn’t classified as an addictive substance, it can still produce a physiological response akin to withdrawal when intake is significantly reduced.
Understanding sugar withdrawal is crucial for anyone looking to curb their sugar consumption. Instead of feeling overwhelmed by the withdrawal process, it’s beneficial to manage expectations and approach reduction in a measured way. Experts recommend monitoring sugar intake through careful reading of labels and making small adjustments to dietary habits, which can minimize the discomfort commonly associated with sugar withdrawal.
Sugar Addiction vs. Sugar Consumption: Key Differences
It’s important to distinguish between sugar addiction and general sugar consumption. While sugar can indeed create a desire for more due to its effects on brain chemistry, most experts agree that it does not exhibit the same clinically defined addiction traits as substances like nicotine or alcohol. This means that while people may develop habits that resemble addiction, the outcome of reducing or eliminating sugar can be vastly different than with genuine addictive substances.
Nevertheless, the societal problem of excessive sugar consumption remains a significant health concern. With health organizations recommending strict limits on added sugars, understanding the distinction between addiction and consumption is crucial. This awareness helps inform better dietary choices and promotes healthier lifestyles without the stigma associated with addiction.
Understanding Sugar Cravings: The Psychological Component
Sugar cravings might be partly psychological, influenced by mood and environmental factors. When individuals face stress, they often turn to comfort foods, many of which are sugar-laden. This behavior suggests that cravings can stem from emotional triggers, demonstrating that the relationship with sugar is not solely based on physiological dependence but also on mental health and emotional regulation.
Addressing sugar cravings effectively requires exploring these psychological factors. Mindfulness, stress management, and healthy coping mechanisms can aid in managing cravings. By recognizing emotional triggers and engaging in healthier alternatives, individuals can build a more robust relationship with food, minimizing the need for sugar-driven comfort.
How to Manage Sugar Intake Effectively
Managing sugar intake is essential for maintaining good health, especially given the staggering statistics on sugar consumption. A clear and structured approach can help individuals make informed choices about their sugar intake while still enjoying their favorite foods. This includes reading labels carefully to monitor added sugars and opting for whole foods over processed ones, which often contain hidden sugars.
Additionally, making gradual changes rather than drastic cuts can facilitate a smoother transition toward a lower sugar diet. For example, reducing sugar in beverages before adjusting food options can create small success experiences, building confidence over time. This method minimizes withdrawal symptoms, making the management of cravings more sustainable.
The Role of Sugar in a Balanced Diet
Despite the debates surrounding sugar’s addictive qualities, it is essential to acknowledge that sugar plays a role in a balanced diet. Natural sugars found in fruits and dairy are part of a healthy eating pattern. The differentiation between added sugars and naturally occurring sugars is crucial; moderation is key in consumption of the former to ensure health benefits without adverse effects.
Incorporating moderate amounts of sugar can enhance flavor and enjoyment of foods without leading to negative health impacts. The American Heart Association suggests that men limit added sugar to 9 teaspoons and women to 6 teaspoons daily, which can make a significant difference in health outcomes. Learning to enjoy the natural sweetness of whole foods can help satisfy cravings in a healthier way.
Exploring Health Risks Related to Excess Sugar Consumption
The health risks associated with excessive sugar consumption are well-documented, linking high intake to obesity, diabetes, heart disease, and more. This emphasizes the importance of monitoring sugar intake in daily diets, as the average American’s sugar consumption far exceeds the recommended limits. Being aware of these health risks can motivate individuals to adopt healthier eating practices.
Furthermore, greater awareness of how sugar impacts overall health encourages proactive choices. Reducing reliance on sugary foods not only aids in managing weight but also contributes positively to mental health and well-being. Familiarity with sugar’s effects empowers individuals to take charge of their dietary habits.
The Connection Between Sugar and Emotional Eating
Many people turn to sugar when feeling stressed or sad, highlighting the connection between sugar and emotional eating. Understanding this relationship is critical for those who wrestle with cravings that arise during emotional turmoil. Recognizing why certain situations prompt cravings allows individuals to work through their feelings without using sugar as a coping mechanism.
Implementing alternative strategies such as physical activity, social engagement, or mindfulness practices can help break the cycle of emotional eating. By cultivating healthier relationship patterns with food, individuals can mitigate the need for sugar-laden comfort foods to cope with emotions.
Creating a Sustainable Sugar Consumption Guide
Creating a sustainable sugar consumption guide can serve as a beneficial tool in managing dietary habits. This guide could include practical tips on how to reduce added sugars, legal insights on reading labels, and examples of healthier alternatives. Educating oneself on the sugar content in various foods aids in making better choices, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes.
Furthermore, maintaining flexibility within your dietary framework can enhance long-term success. Allowing occasional treats while practicing moderation can prevent feelings of deprivation, making it easier to adhere to a healthier sugar consumption guide. Emphasizing balance ensures that sugar does not dominate one’s diet but remains a part of a varied and nutritious eating plan.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like nicotine and alcohol?
While sugar can increase cravings and lead to compulsive eating behaviors, it is not classified as an addictive substance like nicotine or alcohol. The psychological and physical effects of sugar, including withdrawal-like symptoms upon cessation, are real, yet significantly less severe than those associated with true addictive substances.
What are the effects of sugar on the brain?
Sugar consumption can activate the brain’s reward system, similar to how drugs do. This can lead to sugar cravings and habitual consumption of sweet foods, which may result in a dependency-like behavior even though it does not meet clinical addiction criteria.
What are common sugar withdrawal symptoms?
When people suddenly reduce or eliminate sugar from their diets, they can experience withdrawal symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, anxiety, and irritability. These symptoms arise as the body adjusts to lower sugar levels, but they tend to be milder compared to those from substance dependencies like alcohol or drugs.
How can I manage sugar cravings effectively?
Managing sugar cravings can be done by gradually reducing sugar intake instead of stopping abruptly, which could trigger intense cravings. Focus on incorporating natural sources of sweetness, like fruits, while being mindful of added sugars in processed foods.
What is a healthy sugar consumption guide?
The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar to no more than 9 teaspoons per day for men, 6 teaspoons for women, and even lower for children. Being aware of food labels and choosing healthier options can help manage overall sugar consumption effectively.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Sugar’s Addictive Nature | While sugar increases cravings and compulsive eating, it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. |
| Physical and Psychological Effects | Cutting out sugar can lead to withdrawal-like symptoms, though less severe than those from addictive drugs. |
| Dietary Sugar Needs | Sugar is essential in moderate amounts as it’s found in many healthy foods like fruits and dairy, unlike drugs which can be eliminated. |
| Recommended Sugar Intake | The American Heart Association advises limiting added sugars to 9 teaspoons for men, 6 for women, and less for children. |
| Gradual Reduction | Going cold turkey from sugar can be counterproductive; gradual reduction is recommended. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This is a topic that invites significant debate, as sugar elicits cravings similar to those of addictive substances. However, it’s crucial to recognize that while sugar can lead to compulsive eating behaviors, it does not meet the strict criteria to be classified as an addictive substance like nicotine or alcohol. Understanding the distinction between necessary dietary sugars and those in ultra-processed foods can help individuals make healthier choices and manage their intake effectively.