The Alzheimer’s early detection test represents a breakthrough in understanding and managing cognitive decline. Researchers from Mass General Brigham have developed a novel olfactory test that allows individuals to assess their risk for Alzheimer’s disease years before symptoms arise. This at-home test for memory loss evaluates one’s ability to identify and discriminate between different scents, providing crucial insights into early cognitive impairment. Early detection of these symptoms is vital, as it opens the door for timely interventions that can significantly alter the trajectory of neurodegenerative disease progression. By focusing on olfactory dysfunction as a potential marker, this innovative approach bridges the gap between detection and proactive health management for aging populations.
Introducing a novel solution for cognitive health, the Alzheimer’s early detection assessment highlights the significance of smell in identifying early signs of cognitive impairment. This proactive home test for memory assessment delivers critical feedback on individuals’ olfactory discrimination abilities, offering a glimpse into their neurodegenerative status. With an increasing emphasis on preventing the onset of Alzheimer’s through early recognition, tools like the olfactory test for Alzheimer’s hold promise. By shifting the focus towards detecting cognitive decline before it manifests in memory issues, researchers aim to transform approaches to neurodegenerative disease detection. This progressive screening method empowers individuals to take charge of their cognitive health and opens possibilities for timely intervention.
The Role of Olfactory Tests in Alzheimer’s Early Detection
Olfactory testing has emerged as a groundbreaking tool in the early detection of Alzheimer’s disease. These innovative tests assess individuals’ ability to identify and discriminate between different odors, providing crucial insights into cognitive impairment. Recent research indicates a strong correlation between olfactory dysfunction and the onset of neurodegenerative diseases, suggesting that subtle changes in smell could signal deeper cognitive issues long before memory loss becomes apparent. By implementing an at-home olfactory test for Alzheimer’s, individuals can monitor their cognitive health in a comfortable environment, making early detection more accessible.
The significance of this olfactory test for Alzheimer’s lies in its potential to facilitate timely interventions. Early detection not only enhances our understanding of the disease progression but also opens doors to proactive strategies that could slow down cognitive decline. As studies suggest, older adults experiencing olfactory challenges often score lower on these tests, which correlates with early signs of cognitive impairment. This home test could serve as a cost-effective, noninvasive screening method that empowers individuals to take control of their brain health.
Understanding Cognitive Impairment and Its Symptoms
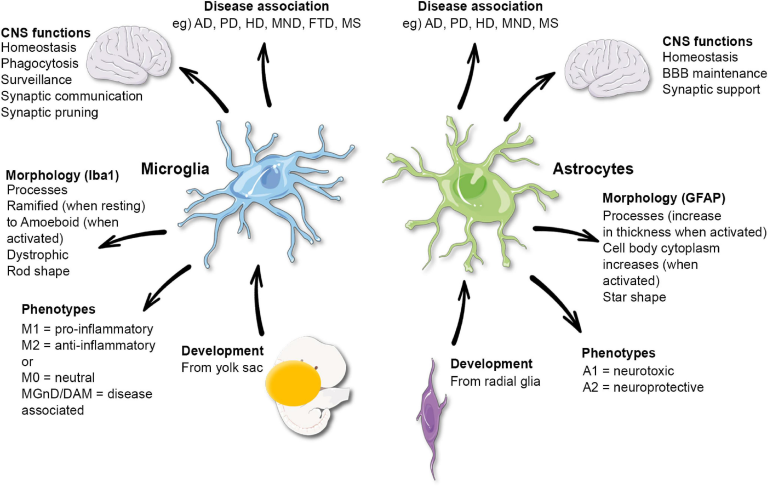
Cognitive impairment encompasses a range of conditions affecting memory, reasoning, and social abilities. Among the most concerning is Alzheimer’s disease, a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive cognitive decline. Symptoms may include forgetfulness, confusion, and difficulty with language, all of which can significantly impact daily living. The challenge lies in identifying these symptoms early, as timely recognition could lead to more effective treatments. Given the intimate link between neurological health and olfactory function, awareness around the scent-based tests becomes increasingly vital for early identification of cognitive issues.
Recognizing the early signs of cognitive impairment not only aids individuals in seeking necessary medical help but also provides families with the opportunity to understand and adapt to their loved ones’ changing abilities. Cognitive decline is not an inevitable part of aging; rather, it can signal the onset of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Utilizing home tests for memory loss, such as the olfactory test, can be a proactive approach for people concerned about their cognitive health.
The Impact of Memory Loss Home Tests
Memory loss home tests play a crucial role in the early detection of cognitive impairment. They empower individuals to take charge of their brain health from the comfort of their homes, allowing for timely monitoring and intervention. Tests such as the olfactory assessment provide an innovative way to gauge cognitive function, specifically targeting the sensory decline often seen in neurodegenerative diseases. This approach is particularly beneficial for those who may be hesitant to visit healthcare facilities for testing, as the results can inform them of necessary steps to take regarding their cognitive health.
Furthermore, the growing accessibility of at-home tests may reduce the burden on healthcare systems while simultaneously enabling more individuals to become aware of their cognitive status. Early identification of memory loss symptoms paves the way for possible lifestyle adjustments, therapeutic interventions, and supportive care. The evolution of home testing represents a significant shift in the landscape of cognitive health, potentially transforming how we approach the management of Alzheimer’s and related disorders.
Advancements in Neurodegenerative Disease Detection
Recent advancements in neurodegenerative disease detection have marked a significant leap forward in our understanding and management of cognitive conditions such as Alzheimer’s. Researchers are continually exploring new methodologies, with olfactory testing emerging as a pivotal strategy in identifying cognitive impairment. Tools such as the Aromha Brain Health Test are at the forefront of this research, allowing for early prediction of neurodegenerative diseases by examining olfactory function. This allows for a nonintrusive way to assess brain health and engage in meaningful discussions about potential future care.
As technology and research methods evolve, there is increasing promise in developing more comprehensive approaches to detect Alzheimer’s symptoms even before they fully manifest. Integrating various assessment tools, including neuropsychological testing alongside olfactory assessments, may provide a clearer picture of cognitive health. This multidimensional approach enables healthcare providers to design tailored interventions based on individual needs, marking a transformative period in the fight against neurodegenerative diseases.
The Connection Between Smell and Memory
The connection between smell and memory has been a subject of fascination within the realms of neuroscience and psychology. It is well-documented that our sense of smell can evoke powerful memories, which in turn can serve as indicators of cognitive health. In the context of Alzheimer’s disease, a decline in olfactory ability may signal early cognitive impairment. With ongoing research backing the olfactory test for Alzheimer’s, understanding this connection can lead to effective screening methods for identifying individuals at risk.
Tailored olfactory tests not only provide a means for early detection but also exemplify the deeper interplay between sensory experiences and cognitive function. By evaluating individuals’ abilities to recognize and remember scents, researchers believe they can glean valuable data about the onset of cognitive decline. This emerging understanding lays the groundwork for broader applications in cognitive health assessments, making it a crucial area of research in the quest to mitigate the effects of neurodegenerative diseases.
Developing Effective Cognitive Screening Tools
The development of effective cognitive screening tools, particularly those suitable for at-home use, has gained traction in light of the rising prevalence of neurodegenerative diseases. An increasing number of studies emphasize the importance of noninvasive, easily accessible testing methods to detect cognitive impairment early. These tools can empower individuals to assess their brain health without the need for clinical interventions, promoting greater awareness and proactive management of cognitive decline.
Among these advances, the olfactory test stands out as a promising method for identifying Alzheimer’s and other cognitive impairments. By turning a simple sensory task into a potential diagnostic tool, researchers aim to create a screening method that is both reliable and user-friendly. As more people familiarize themselves with these self-administered tests, the potential for early intervention and lifelong brain health management increases, significantly impacting public health outcomes.
Cultural Considerations in Cognitive Impairment Testing
Cultural considerations play a critical role in the development and implementation of cognitive impairment testing. For tests to be effective, they must be tailored to accommodate the linguistic and cultural backgrounds of diverse populations. In the case of olfactory testing for Alzheimer’s, researchers have ensured that participants across different linguistic backgrounds, such as English and Spanish speakers, are included in studies, highlighting the importance of inclusivity in cognitive assessments.
Culturally responsive testing can enhance the accuracy of cognitive impairment diagnoses by accounting for variations in odor recognition and memory associations that may differ from one culture to another. As awareness of cognitive health issues continues to grow, it is essential for researchers and healthcare providers to develop tests that resonate with individuals from diverse communities, thereby fostering broader engagement and understanding of early detection methods.
The Future of Alzheimer’s Research and Testing
The future of Alzheimer’s research is increasingly focused on developing innovative, practical tools for early detection and intervention. The rising interest in olfactory tests is a testament to this shift, as it combines neuroscience with practical applications that can be performed at home. Researchers are optimistic that ongoing studies will refine these testing methods, leading to breakthroughs in how we understand and combat cognitive impairment associated with Alzheimer’s disease.
Furthermore, as technology continues to advance, there is the potential to integrate these olfactory tests with other diagnostic platforms, creating a comprehensive approach to monitoring cognitive health. The goal remains to establish reliable methods that not only identify individuals at risk but also provide valuable data for enhancing treatment strategies. With a collaborative effort from researchers, health professionals, and patients, the future of Alzheimer’s research can pave the way for improved outcomes in cognitive health.
Integrating Home Testing into Regular Healthcare Practices
Integrating home testing into regular healthcare practices represents a significant shift in the approach to cognitive health management. As at-home assessments gain popularity, they provide a pathway for individuals to monitor their cognitive function seamlessly within their daily routines. The olfactory test for Alzheimer’s is a prime example of how healthcare can evolve, encouraging regular self-checks that may alert individuals to early signs of cognitive impairment, prompting them to seek further evaluation or intervention.
This newfound convenience aligns with a larger trend towards personalized healthcare, where patients take more active roles in managing their own health. Incorporating home tests into regular check-ups and discussions with healthcare providers can encourage proactive health measures, helping to bridge the gap between individual awareness and medical support. Ultimately, this integration can lead to more timely interventions and improved health outcomes for individuals at risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the olfactory test for Alzheimer’s early detection?
The olfactory test for Alzheimer’s early detection is a home-based assessment where participants identify and memorize different scents. This simple test aims to detect cognitive impairment by evaluating one’s sense of smell, which may decline with neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
How effective is the home test for memory loss in detecting Alzheimer’s symptoms?
The home test for memory loss has shown effectiveness in detecting Alzheimer’s symptoms by assessing olfactory function. Research indicates that older adults with cognitive impairment score lower on this test compared to cognitively normal individuals, making it a promising tool for early detection.
Can an olfactory test help in detecting Alzheimer’s symptoms before they appear?
Yes, an olfactory test can help in detecting Alzheimer’s symptoms years before they manifest. By evaluating one’s ability to identify and memorize scents, researchers believe this test can identify individuals at risk, allowing for early interventions.
What are the benefits of using a test for cognitive impairment at home?
The benefits of using a test for cognitive impairment at home include convenience, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to perform the test without the need for professional supervision. This facilitates widespread access to early detection methods for Alzheimer’s disease.
How can olfactory dysfunction indicate neurodegenerative disease detection?
Olfactory dysfunction can indicate neurodegenerative disease detection by serving as an early warning sign of cognitive decline. Studies have shown that a diminishing sense of smell is correlated with conditions like Alzheimer’s and other cognitive impairments.
What role does the Aromha Brain Health Test play in Alzheimer’s early detection?
The Aromha Brain Health Test plays a significant role in Alzheimer’s early detection as it is an olfactory test designed to identify cognitive impairment risks. Developed by researchers, this test has shown promising results in differentiating between cognitively normal and impaired individuals.
Are there any language considerations for the Alzheimer’s early detection test?
Yes, research indicates that the olfactory test for Alzheimer’s early detection is effective across different languages, as demonstrated in studies with both English and Spanish-speaking participants. This allows for broader application in diverse populations.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Olfactory Tests Developed | These tests assess the ability to smell and identify odors, indicating cognitive health. |
| At-Home Testing | Participants can perform the test in their homes, promoting accessibility. |
| Participants for the Study | Both English and Spanish speakers with cognitive complaints and mild cognitive impairment were included. |
| Correlation with Cognitive Decline | Older adults with cognitive impairment performed worse on olfactory tests than those cognitively normal. |
| Potential for Early Detection | Identifying olfactory dysfunction could indicate risks for Alzheimer’s and other neurodegenerative diseases. |
| Future Research Directions | Further studies may explore long-term effects and incorporate neuropsychological testing. |
Summary
The Alzheimer’s early detection test, utilizing olfactory assessments, represents a significant advancement in identifying individuals at risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease before symptoms manifest. By linking the ability to recognize and remember scents with cognitive health, researchers have created a noninvasive, accessible method for early intervention. This innovative approach not only offers hope for earlier diagnosis but also sets the stage for future research and treatment advancements in combating Alzheimer’s and related neurodegenerative conditions.