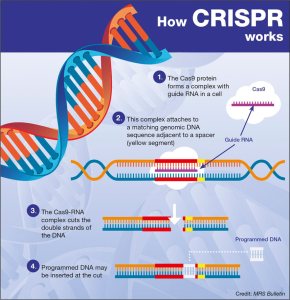
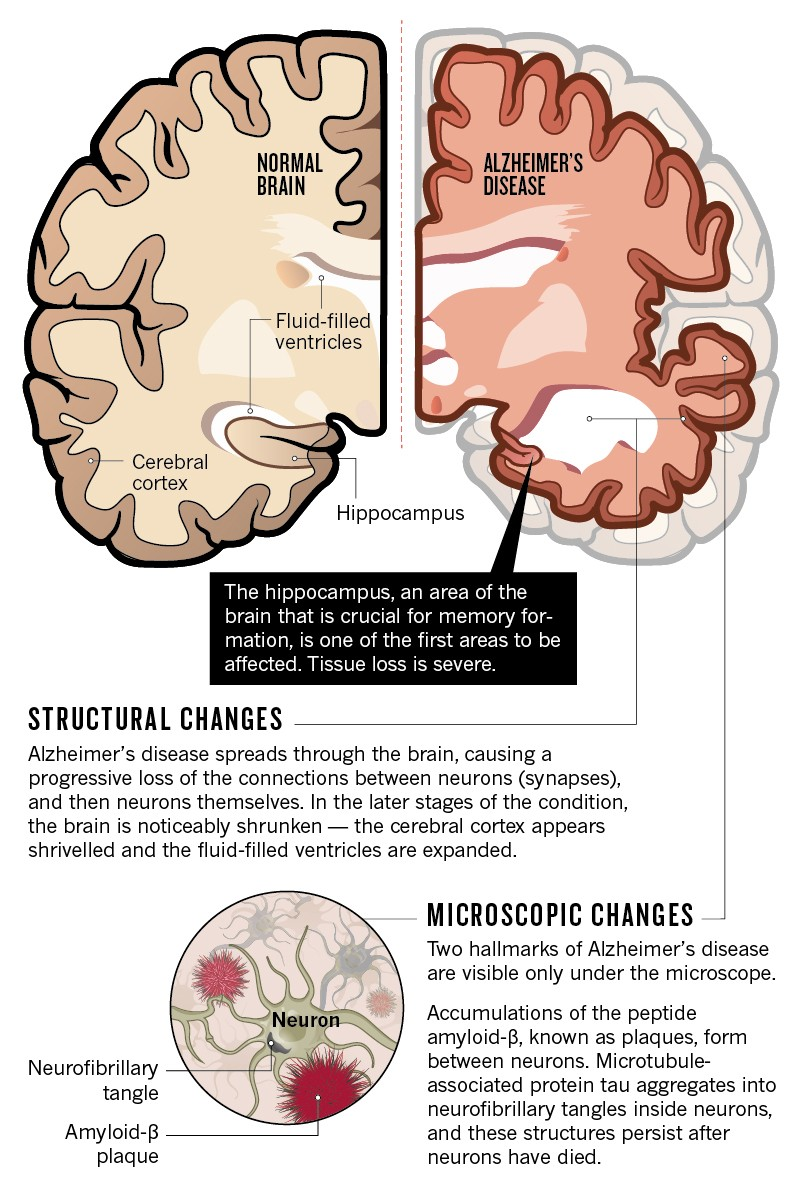
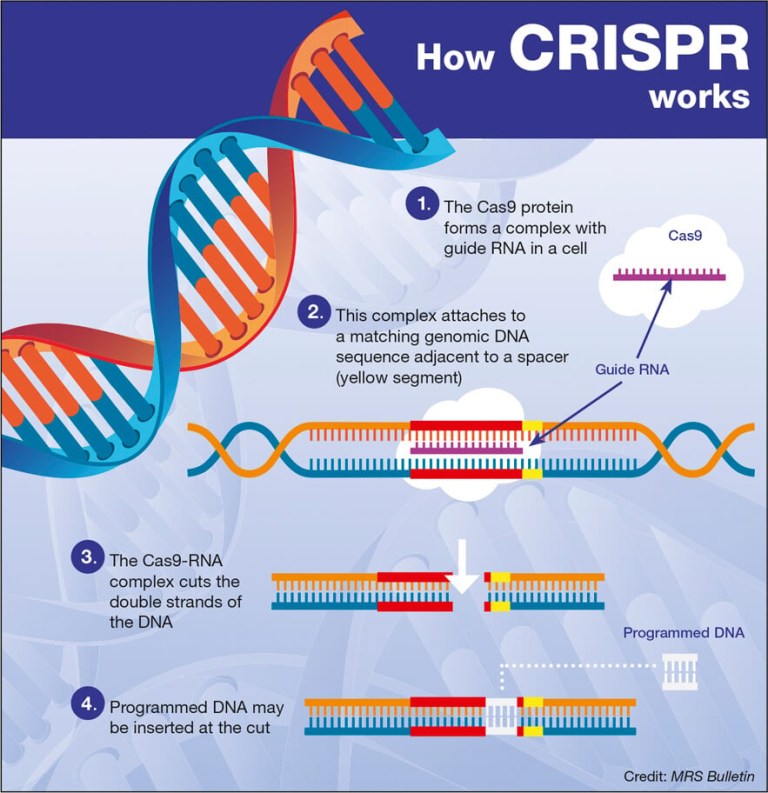
Age-related brain diseases, including stroke, dementia, and late-life depression, pose significant challenges as the global population ages. Recent research has uncovered 17 modifiable risk factors that can dramatically reduce the likelihood of developing these debilitating conditions. Factors such as high blood pressure, poor diet, and low physical activity are linked not only to cognitive decline but also to general brain health improvements. Elevating awareness around dementia and fostering stroke prevention strategies are crucial for enhancing quality of life in older adults. As we better understand these interconnected risks, proactive approaches can make a profound difference in brain health and overall well-being.
As individuals age, they increasingly face various neurological conditions often referred to as cognitive decline disorders or geriatric brain ailments. These issues are interconnected and highlight the importance of addressing shared risk factors among them. Understanding terms like cognitive impairment, neurodegeneration, and mental health deterioration can help frame discussions on prevention. Strategies aimed at improving cognitive function and managing lifestyle choices are essential for combating age-related brain diseases. Through a focus on holistic health and robust research, there is hope for fostering better outcomes for those affected.
Understanding Age-Related Brain Diseases
Age-related brain diseases encompass a range of neurodegenerative conditions such as dementia, stroke, and late-life depression that disproportionately affect older adults. As we age, the risk of developing these illnesses increases significantly, highlighting the need for proactive health measures. These diseases not only impact cognitive function but also affect the quality of life, leading to increased dependency and emotional distress. Understanding the interplay between these conditions is vital for developing effective prevention strategies.
Researchers have demonstrated that age-related brain diseases are interconnected, with overlapping risk factors contributing to their onset. For instance, high blood pressure, diabetes, and obesity are common threads among stroke and dementia patients. By focusing on preventive measures and recognizing these interconnections, individuals can adopt healthier lifestyles that may mitigate the risks associated with multiple conditions, ultimately promoting better brain health and overall well-being.
The Role of Modifiable Risk Factors in Stroke Prevention
Modifiable risk factors are critical for preventing strokes, which remain one of the leading causes of death and disability worldwide. Factors such as high blood pressure, poor diet, and excessive alcohol use can significantly increase the likelihood of experiencing a stroke. By addressing these factors through lifestyle changes—such as maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and moderating alcohol intake—individuals can dramatically reduce their stroke risk.
Recent studies have shown that even reducing one modifiable risk factor can lead to substantial benefits, not just for stroke prevention but also for reducing the risk of dementia and late-life depression. Simple changes, like adopting a healthier lifestyle and managing stress levels, can improve not only cardiovascular health but also cognitive function as we age. The emphasis on managing these risk factors is vital for public health initiatives aiming to combat age-related brain diseases.
Importance of Dementia Awareness
Dementia awareness is crucial in addressing the growing prevalence of cognitive decline among the aging population. Public education about the symptoms, risk factors, and strategies for early intervention can empower individuals and families to seek help sooner, potentially delaying disease progression. Awareness campaigns can also alleviate the stigma surrounding dementia, encouraging open conversations and promoting a more supportive environment for those affected.
Moreover, increasing awareness can lead to greater recognition of the modifiable risk factors associated with dementia, such as hypertension, sedentary lifestyle, and social isolation. Initiatives targeting these areas can encourage preventive measures, making aging individuals more proactive in their health concerns. For example, educational programs that bridge knowledge about diabetes management with strategies for enhancing brain health could lead to comprehensive care approaches that prioritize mental well-being.
Addressing Late-life Depression as a Modifiable Risk Factor
Late-life depression is often overlooked yet plays a significant role in the health outcomes of older adults. This condition can complicate the management of chronic diseases and exacerbate cognitive decline, making it important to address it as a modifiable risk factor. Studies have shown that engaging socially, maintaining a routine, and treating underlying health issues can significantly improve mood and, in turn, cognitive function.
There is a strong correlation between depression and the risk of developing other age-related brain diseases, such as dementia and stroke. By promoting depression awareness and supporting mental health interventions in older populations, healthcare providers can reduce the burden of these interrelated conditions. Programs that focus on social engagement, like community centers offering group activities, can help enhance the emotional well-being of older adults, ultimately fostering better brain health.
Physical Activity: A Key to Brain Health Improvement
Engaging in regular physical activity has been consistently linked to improved brain health and reduced risk of age-related diseases. Exercise helps regulate blood pressure, manage weight, and improve cardiovascular health, which are crucial for preventing conditions like stroke and dementia. Furthermore, physical activity promotes neuroplasticity, allowing the brain to adapt and thrive even as we age.
Incorporating physical activities into daily routines can also enhance mental health by providing a sense of purpose and social connections. Whether through engaging in group exercises or exploring outdoor activities, maintaining an active lifestyle can significantly minimize the risk factors associated with cognitive decline and late-life depression. Not only does this lead to better physical health, but it also fosters a more fulfilling life.
The Impact of Diet on Brain Disease Prevention
Diet plays a pivotal role in brain health, particularly as it relates to the prevention of age-related diseases. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids has been shown to lessen the risk of stroke and dementia. Conversely, diets high in sugar, processed foods, and unhealthy fats may contribute to cognitive decline and other health issues.
Researchers advocate for diets like the Mediterranean or DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) as beneficial for cognitive function. These diets emphasize nutrient-rich foods and can lead to significant improvements in brain health when adopted consistently. Educational initiatives that promote healthy eating habits among older adults can be instrumental in reducing the prevalence of modifiable risk factors leading to age-related brain diseases.
The Connection Between Smoking and Brain Health
Smoking is one of the most significant modifiable risk factors associated with cognitive decline and various age-related brain diseases, including stroke and dementia. The harmful substances found in tobacco smoke can negatively affect blood circulation and contribute to the buildup of plaque in the brain, which is linked to Alzheimer’s disease. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce these risks, leading to improved overall health and brain function.
Public health campaigns aimed at reducing smoking rates among older adults can have profound effects on brain health. Support systems, such as counseling and nicotine replacement therapies, can assist individuals in their journey toward quitting. By spreading awareness about the direct correlation between smoking cessation and enhanced cognitive health, more individuals can be encouraged to make positive lifestyle changes that contribute to their brain’s longevity.
Social Engagement: Enhancing Cognitive Resilience
Social engagement is a critical factor influencing cognitive health in aging populations. Studies indicate that staying socially active can significantly reduce the risk of depression and dementia. Engaging in meaningful interactions, participating in community activities, and nurturing relationships provide mental stimulation and emotional support that are beneficial for brain health.
Creating opportunities for social engagement, such as clubs or community initiatives tailored for older adults, can help mitigate the risks associated with isolation. By fostering strong social ties and encouraging participation in group activities, we can create a supportive environment that promotes both mental and emotional well-being, thereby reducing the incidence of age-related brain diseases.
Stress Management as a Protective Factor for Brain Health
Chronic stress has been identified as a significant risk factor contributing to various health issues, including late-life depression and cognitive decline. Stress can lead to inflammation and negatively impact brain function, making it crucial to develop effective stress-management techniques. Practices such as mindfulness, meditation, and physical exercise can be instrumental in alleviating stress and promoting a healthier mental state.
Implementing stress-reduction programs in community settings can benefit older adults, providing them with tools to manage stress effectively. By fostering an environment that prioritizes mental wellness and offers strategies for coping with stress, we can enhance resilience against age-related brain conditions. Recognizing the importance of stress management can lead to improved mental health outcomes and a better quality of life for older individuals.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the modifiable risk factors for age-related brain diseases?
Modifiable risk factors for age-related brain diseases such as stroke, dementia, and late-life depression include high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity, smoking, excessive alcohol use, poor diet, lack of physical activity, chronic stress, and social engagement. By addressing these factors, individuals can improve their overall brain health and potentially reduce the incidence of these diseases.
How can I reduce my risk of dementia and stroke?
To lower your risk of dementia and stroke, focus on modifying key factors such as maintaining a healthy diet, managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels, engaging in regular physical activity, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption, and fostering social connections. These lifestyle changes can significantly improve brain health and reduce your chances of developing age-related brain diseases.
Why is brain health improvement important in preventing late-life depression?
Brain health improvement plays a crucial role in preventing late-life depression as many shared risk factors, such as poor diet, lack of physical activity, and chronic stress, can negatively impact mental well-being. By actively working to enhance brain health through lifestyle modifications, individuals can mitigate these risks and promote better mental health outcomes.
What is the Brain Care Score and how does it relate to age-related brain diseases?
The Brain Care Score is a tool developed by researchers at Mass General Brigham to assess and guide efforts aimed at protecting and improving brain health. It incorporates findings on modifiable risk factors for age-related brain diseases, helping individuals identify areas for improvement to potentially reduce their risk of stroke, dementia, and late-life depression.
Can physical activity impact the risk of age-related brain diseases?
Yes, physical activity is a significant modifiable risk factor that can lower the risk of age-related brain diseases, including stroke, dementia, and late-life depression. Regular exercise helps improve blood flow to the brain, reduces stress, and supports overall health, making it an essential component of a brain-healthy lifestyle.
How does social engagement influence the risk of dementia and depression?
Social engagement is a critical factor in reducing the risk of dementia and late-life depression. Maintaining connections with family and friends, participating in community activities, and fostering a sense of belonging have been shown to improve mental health and cognitive functions, thereby lowering the risk of these age-related brain diseases.
What lifestyle changes can improve brain health and prevent age-related brain diseases?
Lifestyle changes that can enhance brain health include adopting a balanced diet, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, managing stress effectively, getting adequate sleep, avoiding smoking, and reducing alcohol consumption. These changes address key modifiable risk factors for age-related brain diseases and contribute to better cognitive function and mental well-being.
What role does stress play in the development of age-related brain diseases?
Chronic stress is a significant modifiable risk factor that can increase the likelihood of developing age-related brain diseases such as dementia and late-life depression. High levels of stress can lead to cognitive decline and exacerbate existing health issues. Therefore, managing stress through techniques like mindfulness, exercise, and social support is crucial for maintaining brain health.
How does diet affect the risk of stroke and dementia?
Diet plays a major role in influencing the risk of stroke and dementia. A poor diet high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats can increase the risk of these age-related brain diseases. Conversely, a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats (like omega-3 fatty acids) is associated with better brain health and lower risks of cognitive decline.
What is the connection between kidney disease and age-related brain diseases?
Kidney disease is a modifiable risk factor that increases the likelihood of developing age-related brain diseases such as stroke, dementia, and late-life depression. Poor kidney function affects overall health and can lead to various complications that negatively impact brain health. Therefore, managing kidney health is essential for reducing the risk of these interconnected conditions.
| Risk Factor | Impact on Age-Related Brain Diseases |
|---|---|
| Diabetes | Risk factor for stroke, dementia, depression |
| Blood Pressure | Major risk factor for all three conditions |
| Kidney Disease | Increases risk of stroke, dementia, depression |
| Fasting Plasma Glucose | High blood sugar risk factor |
| Total Cholesterol | Increases risk of stroke and dementia |
| Alcohol Use | Linked to increased risk of stroke, dementia, depression |
| Diet | Contributes to development of conditions |
| Hearing Loss | Modifiable risk factor for dementia |
| Pain | Increases risk of depression and other conditions |
| Physical Activity | Lack of activity is a risk factor for all three |
| Purpose in Life | Lack contributes to depression |
| Sleep | Poor quality increases risk of depression |
| Smoking | Major risk factor for stroke, dementia, depression |
| Social Engagement | Lack enforces depression and related conditions |
| Stress | Chronic stress increases depression risk |
| Depression | Increases risk of other conditions |
| Obesity | Risk factor for stroke, dementia, depression |
Summary
Age-related brain diseases encompass a range of conditions, including stroke, dementia, and late-life depression, all influenced by shared risk factors. Understanding these factors offers a pathway to potentially reduce the incidence of these diseases through simple lifestyle modifications. Researchers have identified 17 modifiable risk factors which can lower the likelihood of developing these conditions. By focusing on these factors, individuals can play a proactive role in protecting their brain health and improving quality of life as they age.