Maternal mortality in the U.S. has emerged as a significant public health crisis, with alarming rates that continue to rise, particularly among racial and ethnic minorities. The latest research indicates that over 80 percent of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable, yet the U.S. leads high-income nations in maternal mortality rates. Between 2018 and 2022, data revealed a distressing spike in U.S. pregnancy-related deaths, posing urgent questions about the effectiveness of prenatal and postpartum care. Factors contributing to this crisis include chronic health conditions exacerbated by inadequate healthcare systems and persistent racial disparities in maternal health. Addressing these issues is vital to reducing preventable deaths during pregnancy and ensuring safer outcomes for all mothers.
The issue of maternal mortality in America presents a profound challenge, often referred to in terms such as pregnancy-associated fatalities and maternal health inequities. Recent studies highlight the disparities in U.S. pregnancy-related deaths, revealing systemic issues within healthcare that disproportionately affect marginalized communities. Many women face significant risks during their childbearing years due to a lack of comprehensive and effective maternal healthcare, which extends beyond the typical prenatal visits. Moreover, the conversation around postpartum care and the ongoing health challenges that arise in the months following delivery is crucial in understanding the overall maternal mortality rate. Addressing these concerns with strategic policies and healthcare improvements is essential to reversing this troubling trend.
Understanding Maternal Mortality in the U.S.
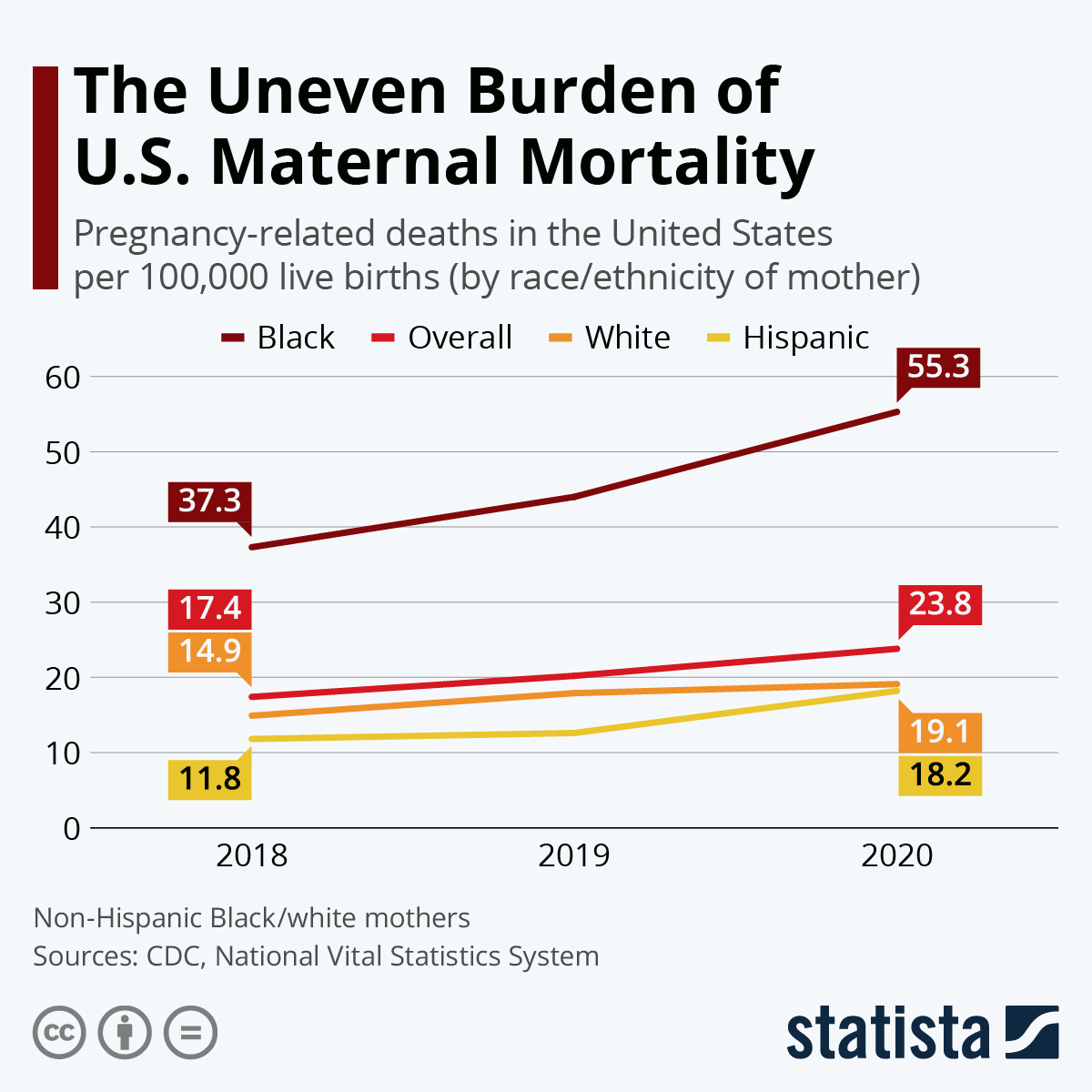
Maternal mortality in the U.S. has become a significant public health concern, especially considering that over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are deemed preventable. Research has highlighted the alarming trends of rising maternal mortality rates, which continue to surpass those of other high-income countries. The statistics paint a grim picture, with the U.S. experiencing around 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births by 2022—up from 25.3 in 2018. The lack of a unified healthcare system and uneven access to quality prenatal care are pivotal factors contributing to this increase.
Moreover, racial and ethnic disparities play a profound role in maternal healthcare outcomes. The findings indicate that American Indian and Alaska Native women suffer the highest mortality rates, highlighting an urgent need for targeted interventions to address these inequities. As various states demonstrate vast differences in maternal mortality rates, understanding and analyzing these disparities is crucial in developing comprehensive strategies aimed at reducing preventable deaths during pregnancy.
The Impact of Postpartum Care on Maternal Health
Postpartum care is often neglected in discussions surrounding maternal health, yet it is a crucial component that influences long-term outcomes for mothers. The findings from recent studies show that late maternal deaths, occurring between 42 days to a year after childbirth, account for nearly one-third of maternal fatalities. It’s apparent that traditional healthcare structures, which focus heavily on the initial six weeks after delivery, are insufficient. Adequate postpartum support is essential for addressing complications such as cardiovascular issues that can arise well after the childbirth experience.
Furthermore, many women may experience chronic conditions that worsen during the postpartum period. Enhancing access to comprehensive postpartum care ensures that mothers receive ongoing evaluations and support, which can significantly reduce the incidence of preventable deaths during this critical time. By investing in better postpartum services and education, we can create a health care continuum that adequately supports mothers not just during pregnancy but throughout their entire reproductive journey.
Racial Disparities in Maternal Health Outcomes
Racial disparities in maternal health outcomes remain a challenging issue within the U.S. healthcare system. Research indicates that non-Hispanic Black women and those from Native American communities face disproportionately higher maternal mortality rates. Systemic factors, such as institutional bias, lack of access to quality healthcare, and socioeconomic barriers contribute to these heightened risks. There is an urgent call for policy changes and healthcare innovations aimed at reducing these disparities, ensuring that all women have equitable access to maternal care.
The persistence of inequities in maternal health outcomes reinforces the need for targeted interventions. Initiatives aimed at understanding the root causes of these disparities could involve community-focused healthcare models that prioritize outreach and education for at-risk populations. Policies that strengthen support for minority groups in maternal health will not only address existing disparities but also foster a more equitable healthcare environment for future generations.
The Role of Chronic Conditions in Pregnancy-Related Deaths
Chronic health conditions such as hypertension and cardiovascular disease have increasingly become leading contributors to maternal mortality in the United States. The recent statistics revealed that nearly 20% of pregnancy-related deaths are attributed to these chronic conditions, underscoring a troubling trend where younger individuals are now facing heightened risks. Addressing these chronic issues necessitates a shift in how healthcare providers approach prenatal and postpartum care, with an emphasis on managing these conditions before and after pregnancy.
There is a pressing need for healthcare systems to implement preventive measures that focus on identifying and controlling chronic conditions among women of reproductive age. This includes routine screenings and educational campaigns aimed at fostering healthier lifestyles. By prioritizing chronic condition management in women’s healthcare, especially for those planning to conceive, we can potentially reduce the rates of preventable deaths during pregnancy and improve overall maternal health outcomes.
The Importance of Public Health Infrastructure for Maternal Health
The current state of maternal health in the U.S. highlights the critical need for a robust public health infrastructure capable of effectively monitoring and addressing pregnancy-related deaths. Given the alarming rise in maternal mortality rates, a renewed focus on funding and resources for public health initiatives is imperative. Without a commitment to bolster these systems, the trajectory of maternal health outcomes will continue to decline.
Investing in public health infrastructure not only aids in tracking maternal health trends but also fosters community engagement and education. Collaborative efforts between government agencies, healthcare providers, and community organizations can lead to the development of comprehensive strategies that target the factors affecting maternal health. These efforts must ensure that policies are informed by data and designed to create equitable healthcare access across all demographic groups.
Innovative Solutions for Reducing Maternal Mortality
There is a growing recognition that innovative solutions are necessary to tackle the rising rates of maternal mortality in the U.S. Many researchers advocate for the implementation of new technologies in prenatal care that can help monitor maternal health more effectively. For instance, the integration of telemedicine can extend care to women in remote or underserved areas, ensuring that they receive timely assessments and interventions.
In addition, education initiatives targeting both healthcare providers and patients are vital for creating awareness around complications that can arise during and after pregnancy. Empowering women with knowledge about their bodies and potential risks can help them advocate for their health needs. With a multi-faceted approach combining technology, education, and community support, the U.S. can make significant strides towards reducing preventable deaths during pregnancy.
Policy Recommendations to Improve Maternal Health Outcomes
To effectively address the crisis of maternal mortality, comprehensive policy reforms at the state and national levels are crucial. Policymakers must prioritize maternal health in their agendas by allocating funding towards research, education, and healthcare access. Measures should include mandating comprehensive training for healthcare professionals on the unique challenges faced by marginalized groups, ensuring that biases do not affect treatment decisions.
Additionally, states can adopt best practices observed in regions with lower maternal mortality rates, such as California. By analyzing successful policies and practices, lawmakers can develop targeted strategies that close the gap in maternal health outcomes across different populations. Continuous monitoring and evaluation of implemented policies will also be necessary to gauge their effectiveness and make data-driven adjustments.
The Rising Challenge of Maternal Mental Health
Maternal mental health is an often-overlooked aspect of maternal care that requires urgent attention. Conditions such as postpartum depression and anxiety can significantly affect a woman’s well-being and her interactions with her newborn, influencing overall health outcomes. Unfortunately, many women do not receive adequate mental health support during and after pregnancy, contributing to a cycle of poor health that can lead to preventable deaths.
Integrating mental health services within the maternal healthcare framework will ensure that women receive holistic support throughout the perinatal period. Training healthcare providers to recognize and address mental health challenges will empower them to offer timely interventions. Furthermore, raising awareness in communities about the importance of maternal mental health can help reduce stigma, making it easier for women to seek help.
Future Directions in Maternal Health Research
Ongoing research into maternal health is critical for understanding and mitigating the factors contributing to rising maternal mortality rates. Future studies should focus on longitudinal approaches to track the health of mothers over time, particularly the long-term effects of pregnancy and childbirth on various demographics. Such research can unveil underlying issues that may contribute to disparities in maternal health outcomes.
Moreover, there is a significant need for studies that emphasize the experiences of marginalized groups within maternal healthcare. Understanding the unique challenges and barriers faced by these populations can inform better service delivery models. Leveraging research findings to advocate for policy changes will be essential in creating a more equitable healthcare system that prioritizes the health and well-being of all mothers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of maternal mortality in the U.S.?
Maternal mortality in the U.S. is primarily attributed to chronic medical conditions, particularly cardiovascular disease, which accounts for over 20% of pregnancy-related deaths. Other significant causes include postpartum hemorrhage and access to inadequate postpartum care. Understanding these causes is crucial in addressing U.S. pregnancy-related deaths.
How does the maternal mortality rate in the U.S. compare to other high-income countries?
The maternal mortality rate in the U.S. is the highest among high-income countries, continuing to rise with 32.6 deaths per 100,000 live births reported in 2022, compared to a rate of 25.3 in 2018. This stark contrast underscores the urgent need for improved prenatal and postpartum care, alongside addressing systemic issues in healthcare.
What role do racial disparities play in maternal mortality in the U.S.?
Racial disparities are significant in U.S. maternal mortality rates, with American Indian and Alaska Native women experiencing the highest mortality at 106.3 deaths per 100,000 live births. Non-Hispanic Black women also face high rates of 76.9 deaths per 100,000 live births, indicating a need for targeted interventions to reduce these inequities in maternal health.
What can be done to reduce preventable deaths during pregnancy in the U.S.?
Reducing preventable deaths during pregnancy in the U.S. requires multiple approaches, including enhancing access to quality prenatal and postpartum care, addressing healthcare inequities, and implementing systemic policy changes. By prioritizing these areas, we can work towards decreasing the maternal mortality rate.
How does postpartum care impact maternal mortality in the U.S.?
Postpartum care plays a critical role in maternal mortality. Many deaths occur after the traditional six-week postpartum visit, indicating that the healthcare system must extend its focus on postpartum care to better support women’s health and address complications that may arise up to one year after childbirth.
Why is it important to track late maternal deaths in the U.S.?
Tracking late maternal deaths—those occurring between 42 days and one year after pregnancy—is vital as it helps in understanding the complete spectrum of maternal health and mortality. The high rates of late maternal deaths highlight the need for continued healthcare access beyond the immediate postpartum period to ensure comprehensive care.
What changes are needed to improve maternal health outcomes in the U.S.?
To improve maternal health outcomes in the U.S., there must be increased investment in public health infrastructure, enhanced targeted solutions for maternal care during and after pregnancy, and reduction of policy disparities among states. Addressing these areas can play a significant role in curbing the high rates of maternal mortality.
What impact did the COVID-19 pandemic have on maternal mortality in the U.S.?
The COVID-19 pandemic had a noticeable impact on maternal mortality in the U.S., particularly in 2021 when rates soared. Although there was a subsequent decrease, the mortality rate in 2022 still remained higher than pre-pandemic levels, indicating that pandemic-related factors contributed to worsening maternal health outcomes.
How can we address the state-level variations in maternal mortality rates in the U.S.?
Addressing state-level variations in maternal mortality rates in the U.S. involves analyzing and understanding the specific factors contributing to these differences. Policymakers can learn from high-performing states like California to implement best practices, prioritize funding for maternal health initiatives, and ensure access to quality care across all states.
What role do chronic conditions play in maternal mortality in the U.S.?
Chronic conditions, such as hypertension and cardiovascular disease, significantly contribute to maternal mortality in the U.S., with younger individuals increasingly experiencing these issues. Addressing and managing these chronic conditions before and during pregnancy is essential to reducing the overall maternal mortality rate.
| Key Points | |
|---|---|
| Rising Maternal Mortality Rates | The U.S. leads high-income countries in maternal mortality rates, with a rise noted between 2018 to 2022, particularly in 2021. |
| Preventable Deaths | Over 80% of pregnancy-related deaths are preventable. |
| Racial and Ethnic Disparities | American Indian and Alaska Native women experience the highest mortality rates. |
| Cardiovascular Disease as Leading Cause | Cardiovascular issues became the leading causes of maternal death, surpassing hemorrhage. |
| Late Maternal Deaths | Nearly a third of maternal deaths occur between 42 days to a year postpartum. |
| Need for Improved Healthcare Systems | Investment in public health infrastructure and addressing state-level disparities is crucial. |
Summary
Maternal mortality in the U.S. continues to be a critical concern, with recent studies revealing alarming rates that starkly contrast with other high-income nations. Over the past few years, significant disparities in maternal health outcomes have been identified, emphasizing the need for urgent systemic reforms and targeted public health investments. The high rate of preventable deaths further underscores the importance of improved prenatal and postpartum care, particularly for marginalized racial and ethnic groups. Without a collective effort to address these disparities and enhance healthcare delivery systems, the troubling trends observed are likely to persist.